Ancient Rome, a civilization known for its vast achievements, stood as a testament to human ingenuity and societal development. With intricate systems of governance, intricate social hierarchies, and elaborate cultural practices, Rome has left an indelible mark on history. From the grandeur of its architecture to the complexities of its economy, Rome's legacy continues to intrigue scholars and enthusiasts alike. But what were the underlying factors that shaped this ancient powerhouse? Let's explore the intricacies of Ancient Rome to uncover the secrets behind its enduring influence on the world stage.
Key Takeaways
- Ancient Rome featured a republican governance structure transitioning to imperial rule under emperors.
- Society was stratified into classes like patricians, equestrians, plebeians, and slaves with limited social mobility.
- Daily life involved early mornings, leisure activities in the afternoons, and elaborate dining customs for supper.
- Entertainment included gladiatorial games, chariot races, theater, public baths, and various leisure activities.
Government and Politics
Ancient Rome's governance structure encompassed a republican system characterized by elected officials and a sophisticated system of checks and balances. At the heart of this system was the Roman Senate, a powerful legislative body comprising wealthy and influential citizens who played a crucial role in decision-making processes. Roman citizens enjoyed the right to vote and participate in political affairs, reflecting a level of inclusivity in governance uncommon for the time.
However, the transition towards an imperial system marked a significant shift in Roman politics. Figures like Julius Caesar and Augustus consolidated power, leading to the concentration of authority in the hands of emperors. This move away from the republican ideals towards a more autocratic rule reshaped the political landscape of Rome and altered the dynamics of governance.
Despite these changes, Roman laws remained a cornerstone of the empire, providing a structured framework for governance and justice that endured through the evolution of political systems.
Social Structure and Classes
Within the societal framework of Rome, distinct social classes delineated the population into stratified groups with defined roles and privileges. At the top of the hierarchy were the patricians, the elite class known for their political power and inherited wealth. Below them were the equestrians, a wealthy business class engaged in commerce and trade. The plebeians constituted the bulk of Roman society, primarily working as farmers, artisans, or laborers, with limited political rights compared to the patricians and equestrians. Slaves occupied the lowest rung, devoid of rights and considered property, serving in various capacities from manual labor to household duties.
Social mobility was significantly constrained in ancient Rome, with rigid boundaries separating the classes based on factors such as birth and wealth. This structured social order shaped every aspect of Roman life, from politics to economics. Understanding the distinct roles and statuses of patricians, equestrians, plebeians, and slaves provides valuable insight into the dynamics of Roman society and the disparities that existed among its populace.
Daily Life and Routine

The daily routines and lifestyle practices of individuals in ancient Rome provide valuable insights into the societal norms and cultural habits prevalent during that time. Romans typically started their day before sunrise, concluding work by noon, and dedicating afternoons to leisure activities such as watching plays and engaging in sports. Public bathhouses were popular venues for relaxation, exercise, socializing, and cleanliness, serving as vital hubs of daily life for Romans. The main meal of the day, supper, was a significant event lasting hours, characterized by elaborate dining customs and multiple courses. Evening entertainment often involved dinner parties featuring music, dancing, and wine, highlighting the importance of social gatherings and leisure in Roman society. Social institutions in ancient Rome emphasized the value of community and shared experiences, contributing to the overall well-being and cohesion of the population.
| Daily Life Practices | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Morning Routine | Starting before sunrise | Establishing productivity |
| Public Bathhouses | Socializing and cleanliness | Promoting community |
| Supper | Elaborate dining customs | Fostering social connections |
| Dinner Parties | Music, dancing, and wine | Enhancing social life |
Entertainment and Leisure
In ancient Rome, entertainment and leisure activities were diverse and engaging. Gladiatorial games and chariot races offered thrilling spectacles for the masses, while Roman theater showcased a variety of dramatic performances. Additionally, social gatherings, games, and relaxation at bathhouses provided Romans with a well-rounded leisure experience.
Roman Entertainment Choices
Exploring the diverse array of entertainment choices available in ancient Rome reveals a society deeply invested in leisure activities that ranged from thrilling spectacles like gladiatorial games to communal experiences at public baths.
- Gladiatorial games and chariot races were popular forms of entertainment, showcasing skills and bravery.
- Romans enjoyed leisure activities like hunting, playing ball games, and attending theater performances.
- Public baths served as social hubs where Romans engaged in exercise, relaxation, and socializing, promoting a sense of community.
Leisure Activities in Rome
Considering the multifaceted nature of Roman leisure activities, it becomes apparent that entertainment and leisure were integral components of daily life in ancient Rome, offering a glimpse into the societal values and preferences of its inhabitants. Various activities catered to different interests, from the thrilling spectacles of gladiatorial games and chariot races to the cultural enrichment provided by theaters. Public baths served not only as places for hygiene but also as social centers where Romans exercised and socialized. The Circus Maximus was the heart of chariot racing, where skilled charioteers competed for glory and fame. Engaging in leisure activities like hunting, fishing, and playing board games allowed Romans to unwind and enjoy moments of relaxation amidst the hustle and bustle of Roman life.
| Leisure Activities | Entertainment Venues | Cultural Enrichment |
|---|---|---|
| Hunting | Circus Maximus | Theaters |
| Fishing | Public Baths | |
| Board Games |
Architecture and Engineering
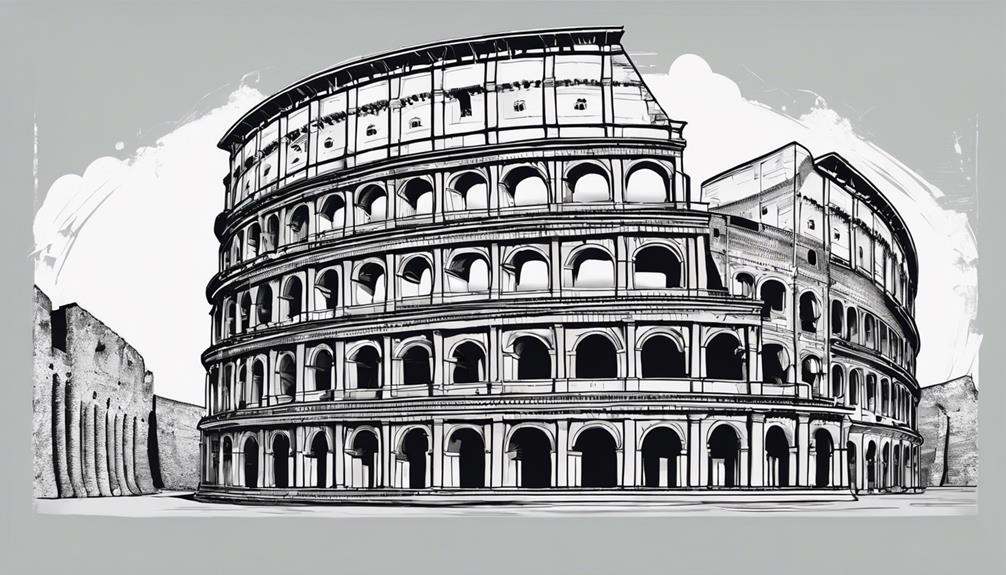

Roman architecture stands as a testament to the engineering prowess of ancient Rome, with structures like the Colosseum showcasing their grandeur and innovation. Aqueducts, designed to transport water from distant sources, highlight the Romans' practical approach to meeting the city's needs. The development of advanced concrete construction techniques further solidified their reputation for durable and monumental architectural achievements.
Roman Colosseum Design
What architectural and engineering marvels characterize the construction of the Roman Colosseum, also known as the Flavian Amphitheater, in ancient Rome during the 1st century AD?
- The Colosseum is a massive elliptical amphitheater built using concrete and sand, showcasing advanced Roman engineering techniques.
- With a seating capacity of approximately 50,000 spectators, the Colosseum featured a sophisticated system of tunnels, chambers, and elevators beneath the arena.
- Its design allowed for efficient crowd control and facilitated a variety of events including gladiatorial contests, animal hunts, and mock sea battles.
Despite centuries of damage and pillaging, the Colosseum stands as a testament to Roman architectural innovation and entertainment, representing a significant cultural and historical icon.
Aqueducts for Water
The intricate network of aqueducts in ancient Rome exemplifies a remarkable fusion of architectural ingenuity and engineering mastery, ensuring the efficient distribution of fresh water across the city. Roman aqueducts were complex systems designed to transport water from distant sources to urban centers without the need for pumps, relying solely on gravity. These structures, utilizing arches, tunnels, and bridges, spanned varied terrains to supply water to public baths, fountains, and residences. The Aqua Marcia, the longest Roman aqueduct at over 56 miles, provided water to Rome, showcasing the advanced infrastructure capabilities of the time. The engineering prowess of these aqueducts not only facilitated water supply but also played a crucial role in maintaining public health through improved sanitation.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Design | Complex systems using arches, tunnels, and bridges |
| Function | Transport water from distant sources to urban areas without pumps |
| Length | Aqua Marcia, the longest aqueduct, stretched over 56 miles to supply Rome |
| Importance | Enabled efficient water distribution for public baths, fountains, and homes |
| Impact | Critical for public health by providing clean water for sanitation |
Innovative Roman Architecture
Exemplifying a harmonious blend of design and functionality, the innovative architectural achievements of ancient Rome stand as enduring symbols of engineering excellence and creative prowess.
- The Pantheon showcased the use of concrete, arches, and domes in Roman architecture.
- Aqueducts were vital engineering marvels designed to transport water over long distances, supplying Roman cities with fresh water for various purposes.
- The Colosseum, an iconic amphitheater, demonstrated advanced engineering techniques in its construction.
Roman architecture not only focused on aesthetics but also prioritized functionality and durability. Public structures like temples, basilicas, and baths reflected the grandeur and sophistication of Roman architectural design. The strategic layout of Roman roads, known for their durability and straight paths, facilitated trade, military movements, and connected cities across the empire.
Military and Warfare

A cornerstone of Ancient Rome's societal structure lay in the meticulous organization and strategic prowess of its military force. The Roman military was renowned for its well-organized legions, each comprising disciplined soldiers equipped with armor, shields, swords, and javelins for combat. Warfare tactics employed by the Romans were highly effective, with the 'testudo' formation being one of the most famous strategies used for protection and advancing towards the enemy.
The success of the Roman military was evident in the numerous conquests and the vast expansion of the Roman Empire. These conquests were made possible by the military campaigns led by skilled Roman generals and soldiers. Additionally, the expertise of Roman military engineers played a crucial role in building impressive fortifications, roads, and siege weapons that further solidified the empire's military might. The combination of strategic thinking, disciplined soldiers, and innovative engineering ensured that the Roman military remained a dominant force in ancient warfare.
| Roman Military | Description |
|---|---|
| Legions | Well-organized units of disciplined soldiers |
| Warfare Tactics | Utilized strategies like the 'testudo' formation |
| Conquests | Led to the expansion of the Roman Empire |
| Military Engineers | Built fortifications, roads, and siege weapons |
| Combat | Equipped soldiers with armor, shields, swords, and javelins |
Religion and Beliefs
Ancient Rome was a society deeply rooted in religious beliefs, with a pantheon of gods and goddesses shaping various aspects of daily life. Religious rituals, festivals, and offerings were central to Roman culture, honoring deities such as Bacchus and Venus. The belief in the afterlife and the worship of household gods like Lares and Penates were significant components of Roman spirituality.
Roman Gods and Myths
Roman religion in ancient times revolved around a complex pantheon of gods and goddesses, embodying various aspects of life and nature.
- Jupiter, Juno, and Mars were prominent deities worshipped by the Romans.
- Lares and Penates were household spirits believed to provide protection and ensure prosperity.
- Myths like the tale of Romulus and Remus, the founders of Rome, played a significant role in shaping Roman identity.
These beliefs influenced daily life, with priests conducting rituals and sacrifices to appease the gods and seek their favor. Festivals such as Saturnalia and Lupercalia were held to honor these deities and celebrate Roman culture. The intricate interweaving of gods and myths in Roman society showcased the importance of spirituality in the lives of its people.
Religious Rituals and Practices
Exploring the intricate religious rituals and practices of ancient Rome reveals a complex tapestry of beliefs and ceremonies that shaped the spiritual landscape of Roman society. Roman religion was polytheistic, with a pantheon of gods such as Jupiter, Mars, and Venus. Augurs, as priests, interpreted divine will through signs. The Vestal Virgins played a crucial role in maintaining the sacred fire of Vesta, symbolizing the hearth of Rome. Emperors often attained divine status after death, intertwining political power with religious beliefs. Sacrifices, prayers, and festivals were common practices to honor and seek favor from the gods. Below is a table summarizing key aspects of Roman religious rituals and practices:
| Aspect | Description | Role in Society |
|---|---|---|
| Vestal Virgins | Keepers of the sacred fire of Vesta | Ensuring the city's prosperity |
| Augurs | Interpreters of divine will through signs | Guiding important decisions |
| Deified Emperors | Emperors elevated to divine status after death | Reinforcing imperial authority |
Beliefs in the Afterlife
Beliefs in the afterlife among the ancient Romans were intricately woven into the fabric of their religious and spiritual worldview. The Romans held several beliefs about the afterlife, shaping their attitudes towards death and rituals surrounding it. Key aspects of Roman beliefs in the afterlife include:
- Judgment of the Soul: Romans believed that the soul would face judgment based on one's deeds in life.
- Underworld Ruled by Deities: The concept of the underworld, governed by gods like Pluto and Proserpina, was central to Roman beliefs.
- Funeral Rituals: Roman funeral practices involved offerings to appease spirits and ensure a peaceful passage to the afterlife.
Economy and Trade
A pivotal aspect of ancient Rome's societal structure was the intricate web of economic activities centered around agriculture, trade, and slave labor. Agriculture played a crucial role in the Roman economy, with farmers utilizing oxen, hand tools, and innovative techniques like crop rotation to produce goods for trade. The Roman conquests expanded their access to valuable resources such as gold, silver, and grain, which in turn fueled economic growth and trade. The government's minting of coins established a standardized currency system that facilitated commerce within and beyond Rome's borders. Trade routes like the Silk Road connected Rome to distant lands, enabling the exchange of goods and cultural interactions.
| Economic Activities | Importance | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Primary economic activity | Crop rotation |
| Trade | Facilitated commerce and cultural exchange | Silk Road |
| Slave Labor | Contributed to economic productivity | Work on farms |
This structured economic system underpinned the prosperity and growth of ancient Rome while also highlighting the reliance on agricultural practices, trade networks, and labor systems to sustain the empire's economy.
Art and Literature

In the realm of ancient Rome, the convergence of artistic expression and literary endeavors bore witness to a rich tapestry of cultural achievements. Roman art, heavily influenced by Greek styles, showcased realistic portrayals of human figures and mythological scenes. Literature flourished in ancient Rome, with epic poems like Virgil's 'Aeneid' and philosophical works by Cicero and Seneca captivating audiences with their depth and insight. Mosaics and frescoes, found in Roman homes and public buildings, displayed intricate designs and vibrant colors, adding a touch of elegance to everyday life. Roman sculptures, known for their emphasis on realism and detail, such as the 'Laocoön and His Sons,' conveyed intense emotions and stories through their craftsmanship. Additionally, Roman architects like Vitruvius left a lasting legacy with their treatises on architectural principles, shaping building designs throughout the empire. The artistic and literary legacy of ancient Rome continues to inspire and captivate audiences to this day.
Decline and Fall
The decline and fall of ancient Rome were precipitated by a combination of political instability, economic challenges, and military setbacks, culminating in significant events that marked the unraveling of a once-mighty empire.
| Factors | Impacts |
|---|---|
| Political Instability | Weak leadership and frequent civil wars destabilized governance, leading to a lack of unity and coherent decision-making. |
| Economic Troubles | Issues like inflation, heavy taxation, and overreliance on slave labor strained the economy, causing widespread discontent among the populace. |
| Military Defeats | Encounters with barbarian tribes, such as the Visigoths and Vandals, weakened the Roman military prowess, leaving the empire vulnerable to external threats. |
| Barbarian Invasions | Continuous invasions and raids by barbarian groups further eroded the empire's defenses and resources, hastening its decline. |
The division of the empire into the Western and Eastern Roman Empires also played a significant role, as it created internal strife and made the empire more susceptible to external pressures. The sack of Rome by the Visigoths in 410 AD and the eventual fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD were pivotal events that signaled the end of ancient Rome's dominance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Was Life Like in Ancient Rome?
Life in ancient Rome was multifaceted, characterized by a complex social hierarchy that dictated daily interactions. Entertainment and education were pivotal aspects of Roman life, with leisure activities like attending plays and engaging in sports. Family structure and food played significant roles in society, while clothing and housing reflected one's status. Religion and politics were intertwined, influencing both personal and public life. The economy and military were crucial for the empire's stability and expansion.
How Would You Describe Ancient Rome?
Ancient Rome, a complex civilization, was marked by a rigid social hierarchy, awe-inspiring architectural marvels, and a history of military conquests. Its political landscape was fraught with intrigue, while daily routines balanced work and leisure. Entertainment options like gladiatorial games and chariot races captivated the populace. These facets, intertwined with distinct gender roles and a patriarchal family structure, painted a vivid picture of life in ancient Rome.
What Are 5 Facts About Ancient Rome?
Ancient Rome was renowned for its sophisticated social structure, efficient government system, formidable military power, breathtaking architectural marvels, vibrant daily life, and groundbreaking technological advancements. These included aqueducts and concrete for construction, Roman roads for trade, and a calendar that influenced modern timekeeping. Citizens engaged in activities like visiting public baths, taverns, and using public toilets, creating a rich tapestry of daily life in the ancient city.
What Was the Culture Like in Ancient Rome?
In ancient Rome, culture was a rich tapestry woven with diverse artistic expressions, reflecting a complex society structured by a strict social hierarchy. Religious practices permeated daily routines, influencing both private and public life. Culinary delights added flavor to gatherings, while a plethora of entertainment options catered to varying tastes. This amalgamation of elements created a multifaceted culture that shaped Roman identity and contributed to the empire's enduring legacy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the grandeur and complexity of Ancient Rome surpassed all known civilizations, with its unparalleled advancements in governance, engineering, and culture. The intricate social hierarchy, innovative architectural feats, and diverse forms of entertainment defined a society that stood as a pinnacle of human achievement. Despite its eventual decline and fall, the legacy of Ancient Rome continues to captivate and inspire scholars and enthusiasts worldwide, showcasing a civilization of unparalleled grandeur and sophistication.
